Investigation and Classification of Inclusions in Grey Cast Iron Castings
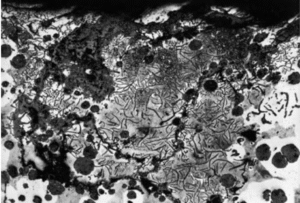
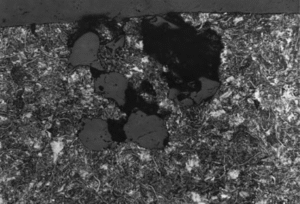
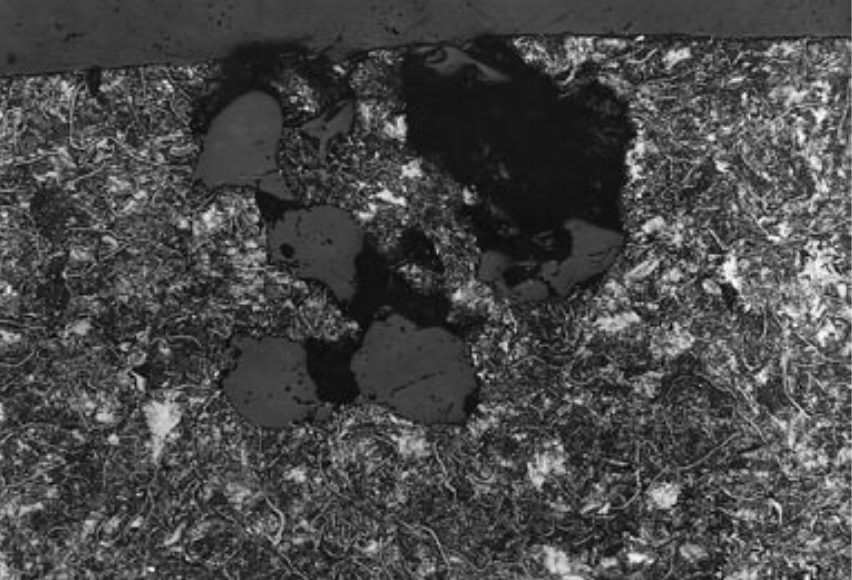
Inclusions are among the most critical casting defects in grey cast iron, and their proper identification and control play a key role in improving part quality and reducing production costs. This article presents a classification of the four main types of inclusions along with methods for their identification and reduction.
1. Slag Inclusions (from Melting and Transfer):
These inclusions result from non-metallic impurities, adhered sand, scrap dust, or slag-forming reactions during melting. They typically appear as porous, irregular masses bonded to the metallic matrix.
Main causes: contaminated scrap, prolonged holding of molten metal, and improper chemical composition.
2. Refractory Inclusions:
These are caused by the detachment of refractory particles from the furnace or ladle lining due to poor refractory quality, high moisture content, or uneven ramming. They resemble slag inclusions and are usually identified by evaluating the timing and quality of the refractory lining.
3. Sand Inclusions:
These are due to the entry of molding or core sand particles into the melt. Under a microscope, they appear as angular, multi-faced particles. Low-strength sand or loose sand in the system increases the likelihood of this defect.
4. Oxide Film Inclusions:
These form as a result of turbulence during pouring, which folds oxidized surface layers into the melt. Microscopically, they appear as thin cracks or bright lines around the defect. Improper gating design and excessive pouring height are the main contributing factors.
Identification Methods:
-
Optical and stereo microscopy
-
EDS analysis
-
Detailed metallographic examinations to determine the location, structure, and chemical composition of inclusions
Recommended Control Measures:
-
Optimized gating system design to reduce turbulence
-
Use of high-quality scrap and molding sand
-
Tight control of molten metal chemistry
-
Minimizing holding time of molten metal
-
Proper refractory lining and controlled inoculant additions
Conclusion:
A clear understanding of inclusion types and their formation mechanisms can help prevent many casting defects and significantly enhance final product quality.
If you are facing issues with surface or subsurface inclusions in your grey or ductile iron castings, feel free to contact our technical team at َARAD FOUNDRY ANALYSIS.
This article was prepared by the R&D Department of Tahlilgaran Zob Arad