The Effect of Titanium on the Mechanical Properties, Microstructure, and Machinability of Grey Cast Iron Castings
Overview
Grey cast iron with flake graphite is one of the most widely used materials in the automotive industry. A key challenge in producing cast iron components is achieving a balance between desirable mechanical properties and economic efficiency. The graphite morphology (shape, size, and distribution) plays a crucial role in determining strength, hardness, and machinability.
Objective
This study investigates the influence of titanium as a trace element on the structure and properties of grey cast iron. Titanium may enter the melt through contaminated scrap, such as painted, galvanized, or enameled materials.
Key Findings
Reduction in Hardness with Titanium Increase:
Experimental results showed that when the titanium content exceeded 0.025 wt%, the hardness dropped by approximately 20 Brinell units. This reduction was attributed to the increased presence of soft ferritic phases in the microstructure.
Changes in Microstructure:
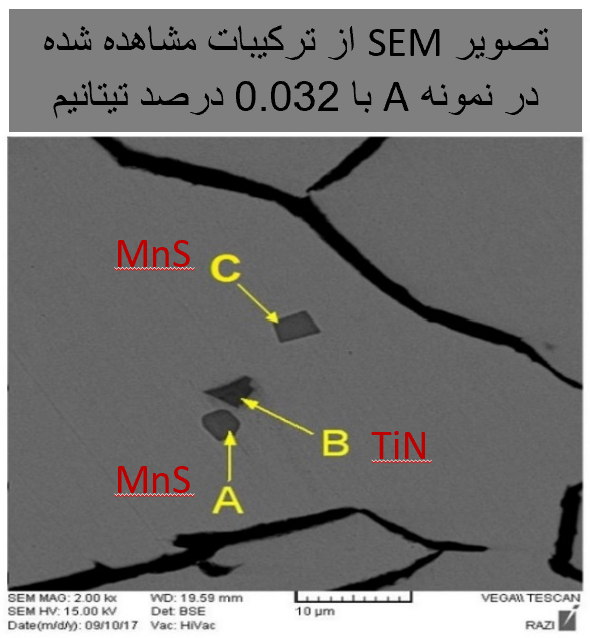
With increasing titanium, the thickness of the ferritic rim from the surface inward increased, and the overall structure shifted from pearlitic to more ferritic. This transformation is due to undercooling effects and the formation of compounds such as titanium carbides and nitrides.
Reduced Machinability:
The presence of hard TiC particles in the structure negatively affected machinability, leading to increased tool wear and resistance to cutting. Cutting tools deteriorated rapidly when in contact with these hard inclusions.
Impact on Tensile Strength:
Although the reduction in tensile strength was relatively limited, samples with higher titanium content exhibited slightly lower tensile strength, particularly near the surface regions enriched with ferrite.
Recommendations for Control:
To prevent unintended titanium contamination, it is recommended to use a controlled charge mix, including high-quality pig iron and selected scrap. Additionally, strict chemical analysis control prior to pouring is essential.
Conclusion
Even small amounts of titanium can significantly impact the microstructure, hardness, machinability, and final production cost of grey cast iron castings. Therefore, precise control during melting and charge preparation is critical.
If you’re facing issues with hardness or tensile strength in cast iron components, feel free to contact our experts at ARAD FOUNDRY ANALYSIS Company. Our technical team is ready to offer professional consulting and practical solutions.